When it comes to serious infections, terms like sepsis and septicemia are often used interchangeably. However, these conditions are not the same. Understanding the difference is crucial, especially because both can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. In this article, we’ll clarify what distinguishes sepsis from septicemia and explain their connections, symptoms, and treatments.
Introduction to Sepsis and Septicemia
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Misunderstanding sepsis and septicemia can lead to delayed treatment or inappropriate care. Knowing the difference ensures better awareness and faster medical intervention.
Common Misconceptions
People often believe that sepsis and septicemia are identical because they are closely related. In reality, septicemia is a specific condition that can lead to sepsis. Let’s break it down.
You May Like:
Speed Up Cold Recovery with These 15 Superfoods
What Is Sepsis?
Definition and Overview
Sepsis is the body’s extreme response to an infection. It occurs when the immune system overreacts to an infection, causing widespread inflammation, tissue damage, and organ failure.
Causes of Sepsis
Sepsis can result from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. Common sources include:
- Urinary tract infections
- Pneumonia
- Skin infections
- Infections following surgery or trauma
Symptoms of Sepsis
Sepsis symptoms often include:
- Fever or hypothermia
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Confusion or disorientation
- Low blood pressure
What Is Septicemia?
Definition and Overview
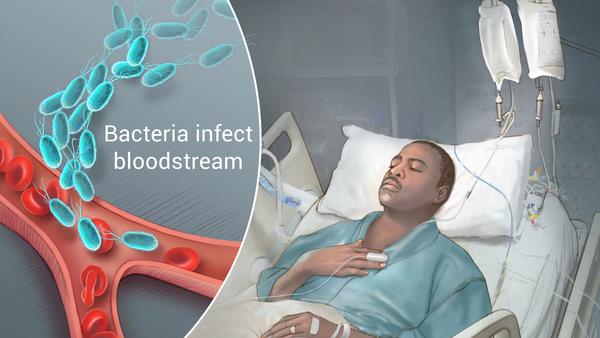
Septicemia, also known as blood poisoning, is a bacterial infection that spreads throughout the bloodstream. It serves as a precursor to sepsis if left untreated.
Causes of Septicemia
Septicemia typically results from localized infections that enter the bloodstream. Examples include infections in the lungs, urinary tract, or abdomen.
Symptoms of Septicemia
Symptoms of septicemia include:
- High fever
- Chills and sweating
- Rapid breathing
- Low blood pressure
- Extreme fatigue
Key Differences Between Sepsis and Septicemia
The Underlying Process
While septicemia refers specifically to a bloodstream infection, sepsis describes the body’s systemic response to that infection. In other words, septicemia can lead to sepsis, but not all sepsis cases involve septicemia.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing septicemia involves blood tests to identify the specific bacteria, while sepsis requires identifying organ dysfunction caused by the infection. Treatments for septicemia focus on eliminating the bloodstream infection, while sepsis treatment aims to stabilize organ function.
Severity and Progression
Septicemia is an infection stage, whereas sepsis represents a more severe condition that affects the entire body. Sepsis carries a higher risk of complications, including septic shock and death.
How Are Sepsis and Septicemia Related?
Septicemia as a Pathway to Sepsis
Septicemia can progress to sepsis when the infection triggers an exaggerated immune response. This progression is why early treatment of septicemia is so vital.
Overlapping Symptoms
Both conditions share common symptoms like fever and low blood pressure, but sepsis also involves signs of organ failure, such as kidney dysfunction or respiratory distress.
Diagnosing and Treating Sepsis and Septicemia
Diagnostic Tools and Methods
Doctors use several tools to diagnose sepsis and septicemia, including:
- Blood cultures to identify bacteria or fungi
- Imaging tests to locate the source of infection
- Blood tests to check for organ dysfunction
Treatment Options
Antibiotics and Supportive Care
Both conditions require antibiotics to eliminate the infection. Supportive care, such as oxygen therapy, IV fluids, and medications to stabilize blood pressure, is essential in sepsis.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients with sepsis or septicemia need close monitoring to ensure treatment effectiveness and prevent complications.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Reducing Infection Risks
Preventing infections through proper hygiene, vaccination, and timely medical care reduces the likelihood of septicemia and sepsis.
Early Detection Strategies
Recognizing the early signs of infection and seeking medical attention promptly can prevent septicemia from progressing to sepsis.
Conclusion
Sepsis and septicemia are serious medical conditions that require urgent attention. While septicemia refers to a bloodstream infection, sepsis is the body’s dangerous response to such infections. Understanding their differences helps in identifying symptoms early and ensuring the right treatment is administered.
By improving awareness and prevention strategies, we can reduce the risks associated with these life-threatening conditions. Always consult a healthcare provider if you suspect an infection or notice worsening symptoms.
FAQs
1. Can septicemia occur without leading to sepsis?
Yes, septicemia can be treated before it progresses to sepsis if detected early.
2. Is septicemia the same as blood poisoning?
Yes, septicemia is commonly referred to as blood poisoning because it involves bacteria in the bloodstream.
3. How is sepsis diagnosed?
Sepsis is diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies, and evaluating organ function.
4. What are the early signs of septicemia?
Early signs include high fever, chills, rapid breathing, and fatigue.
5. Can sepsis be prevented?
Yes, preventing infections through good hygiene, vaccinations, and early medical care reduces the risk of sepsis.